Understanding the Importance of Security Labels
- Share
- publisher
- brain shi
- Issue Time
- May 23,2024
Summary
Safety labels are vital for conveying immediate hazard information, complying with regulations, and safeguarding individuals in workplaces and during product use. They prevent accidents, support traceability, deter counterfeiting, and uphold brand integrity. By adhering to standards like GHS, OSHA, and ISO, these visual cues ensure universal comprehension, facilitating a secure environment globally. Proper labeling reduces liability, facilitates emergency response, promotes a culture of safety.
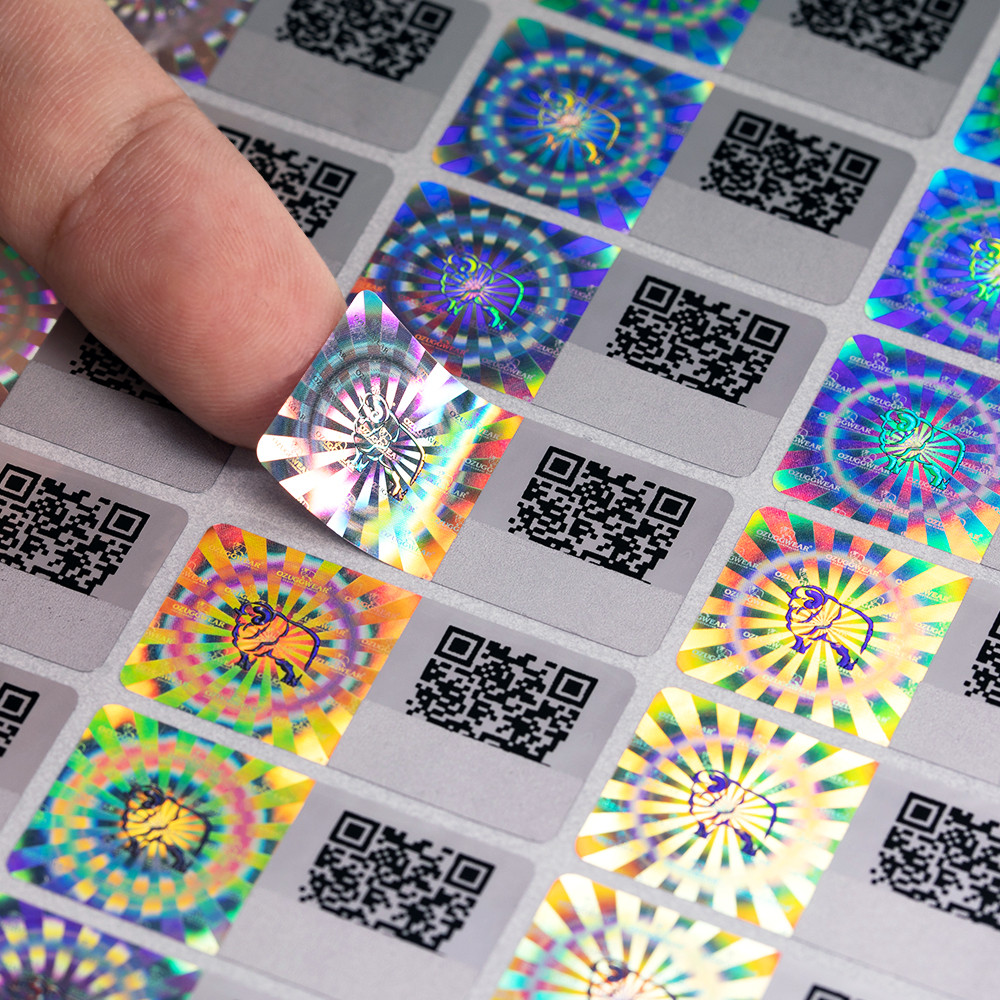

1.Why Security Labels Matter in Today's World
In today's interconnected and security-conscious environment, security labels have become essential tools in the fight against counterfeiting, product tampering, and ensuring consumer trust. These labels serve as a critical line of defense, safeguarding supply chains, and validating product authenticity.
2.Types of Security Labels
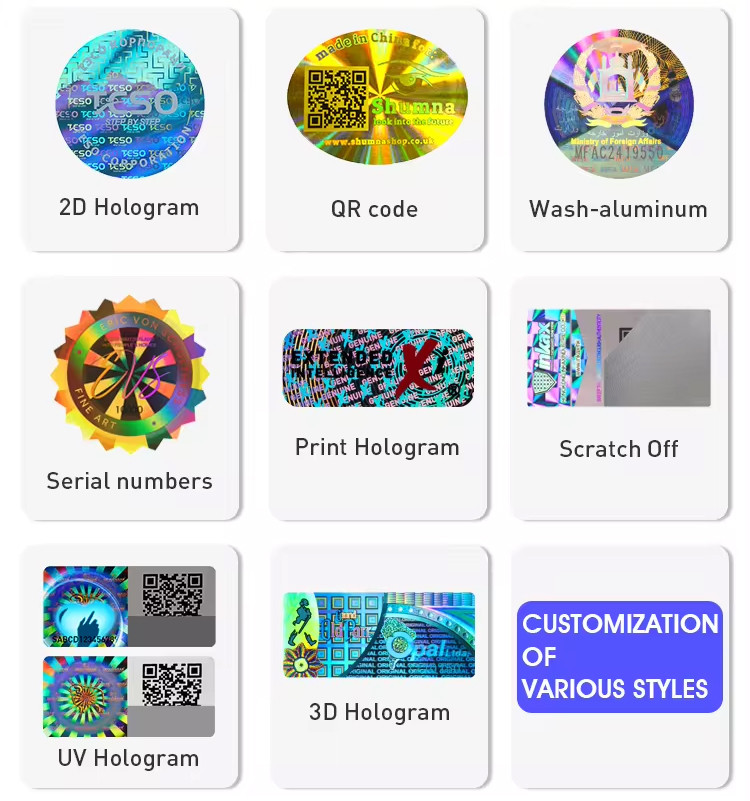
The types of safety labels include:
1. **GHS Labels**: Globally Harmonized System (GHS) labels that comstandardized symbols, signal words, and hazard statements.
municate chemical hazards through
2. **Warning Labels**: General alerts indicating potential dangers or precautions needed when handling products or machinery.
3. **Hazard Symbols**: Pictograms representing specific types of hazards, such as flammable, toxic, corrosive, or explosive materials.
4. **RFID Tags**: Radio Frequency Identification tags used for tracking and security purposes, allowing electronic identification and access control.
5. **Tamper-Evident Seals**: Labels or stickers that show visible signs of any attempt to open or compromise a package or container.
6. **Security Holograms**: Three-dimensional images providing authentication and anti-counterfeiting measures.
7. **Barcodes and QR Codes**: Used for product identification, tracking, and access to additional safety information via scanning.
8. **Temperature Sensitive Labels**: Indicate if a product has been exposed to inappropriate temperatures during storage or transport.
9. ** Serialization Labels**: Unique identifiers for individual items, aiding in traceability and combating counterfeits.
10. **Lockout/Tagout Labels**: Applied during maintenance to ensure machines are not operated unintentionally, preventing accidents.
These labels serve different purposes, sfrom indicating immediate dangers to enabling product tracking and anti-tampering measures, each playing a vital role in ensuring safety and security across various industrie.
3.Benefits of Utilizing Security Labels
1. **Enhanced Safety Awareness**: Clear and conspicuous safety labels immediately draw attention to potential hazards, fostering a culture of caution and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
2. **Compliance with Regulations**: Adhering to OSHA, ANSI, and other international safety standards helps businesses avoid fines and legal liabilities while ensuring worker welfare.
3. **Standardization of Communication**: Standard symbols and warning phrases facilitate universal understanding, transcending language barriers and educational levels.
4. **Product Integrity**: Tamper-evident and authentication labels protect against counterfeiting and product tampering, assuring customers of the product's genuine nature and quality.
5. **Traceability and Recall Efficiency**: Unique identification labels aid in tracking products throughout the supply chain, making recalls more targeted and efficient should a safety issue arise.
6. **Liability Reduction**: Demonstrating due diligence by using safety labels can mitigate legal liability in case of accidents, showing that reasonable precautions were taken.
7. **Brand Reputation**: A commitment to safety through proper labeling enhances brand image and customer trust, as it signals responsibility and care for consumer well-being.
8. **Employee Training Aid**: Safety labels can serve as instructional tools during training, helping employees understand the risks associated with specific equipment or materials.
9. **Insurance Benefits**: Many insurance providers offer better rates or terms to businesses that implement robust safety measures, including the use of safety labels.
10. **Efficient Emergency Response**: In the event of an incident, clear safety labels can guide emergency responders to identify hazards quickly, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
Overall, safety labels contribute significantly to creating a secure environment, fostering trust, and maintaining operational efficiency across industries.
4.Regulations and Standards for Security Labels
Safety labels are governed by various regulations and standards worldwide to ensure consistency and effectiveness in communicating hazards. Some prominent ones include:
1. **GHS (Globally Harmonized System)**: The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals provides a framework for standardized labeling of chemicals to enhance understanding of hazards on a global scale.
2. **OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)**: OSHA, a U.S. regulatory body, enforces several standards related to hazard communication, including 29 CFR 1910.1200 (the Hazard Communication Standard or HCS), which requires chemical manufacturers and importers to provide Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) and appropriate labels.
3. **ANSI (American National Standards Institute)**: ANSI develops and publishes consensus standards for safety signs and labels in the U.S., such as ANSI Z535 series, which covers product safety labels, safety signs, and accident prevention tags.
4. **ISO (International Organization for Standardization)**: ISO standards like ISO 3864 series pertain to graphical symbols, safety colors, and safety signs, providing an international baseline for visual communication of safety information.
5. **REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals)**: A European Union regulation, REACH addresses the production and use of chemical substances, including labeling requirements for substances and mixtures.
6. **CLP (Classification, Labelling and Packaging Regulation)**: This EU regulation aligns with the GHS and governs the classification, labeling, and packaging of chemical substances and mixtures in the EU market.
7. **WHMIS (Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System)**: Specific to Canada, WHMIS requires employers to inform workers about hazardous materials through labels, SDSs, and training, following the GHS system since 2015 (known as WHMIS 2015).
8. **ADR (European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road)**: ADR sets out rules for the transport of dangerous goods by road, including labeling and placarding requirements.
9. **UN Model Regulations**: The United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods serve as a model for international transport, influencing national and regional regulations like ADR, IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code), and ICAO TI (International Civil Aviation Organization Technical Instructions).
These regulations and standards ensure that safety labels provide consistent, recognizable warnings and instructions across different countries and industries, contributing to a safer global work environment.